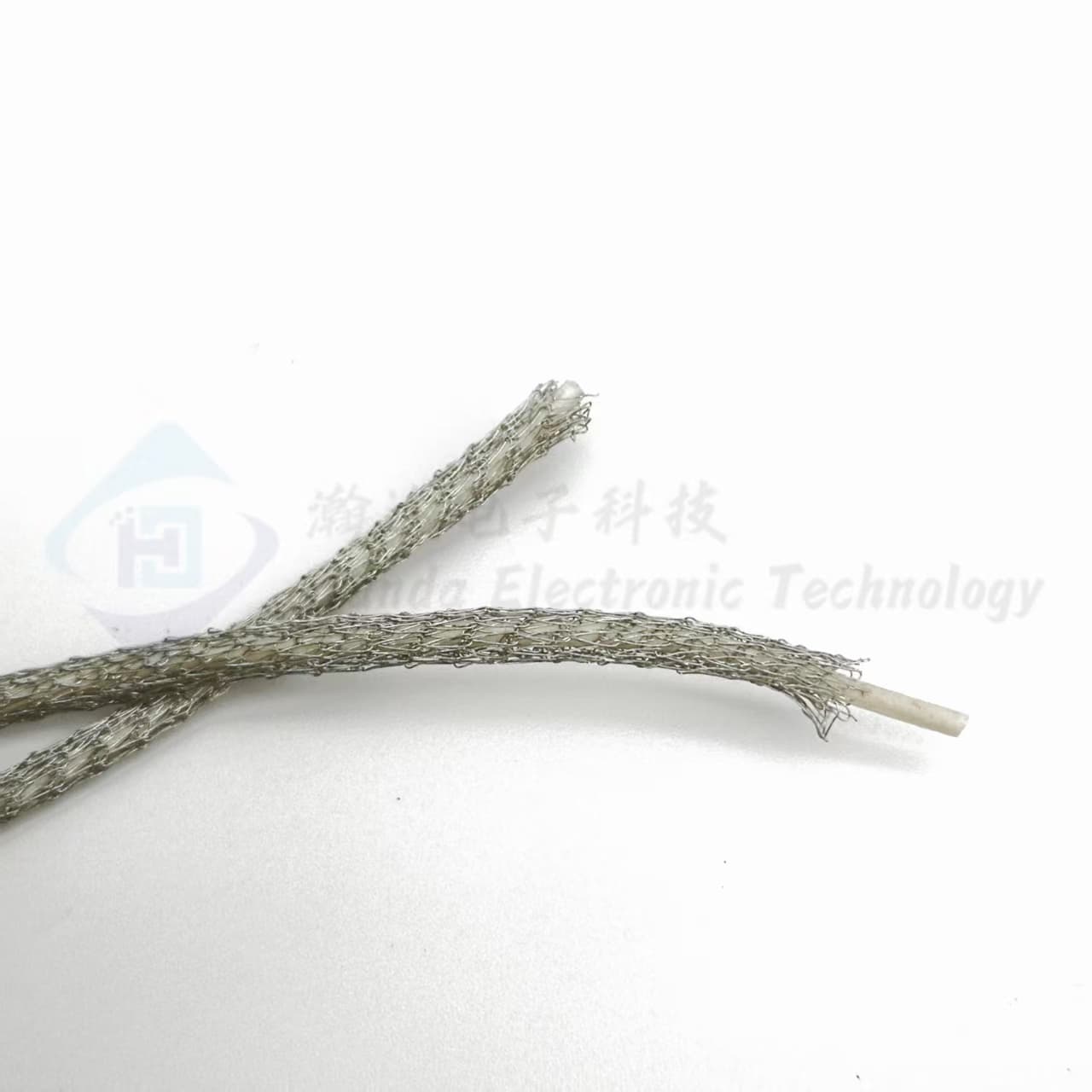
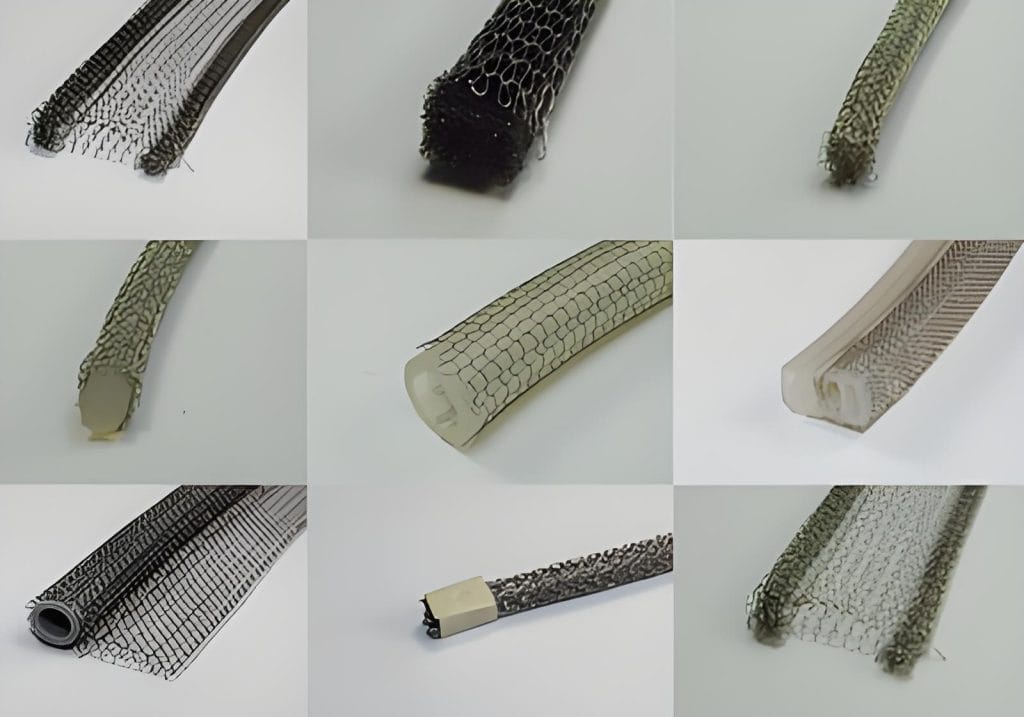
Knitted wire mesh gaskets
Handa knitted wire mesh gaskets are a type of EMI/RFI shielding product used to protect against electromagnetic interference and radio frequency interference.
They consist of a knitted mesh made from conductive wires like tin-copper-steel, aluminum, or monel.The mesh provides effective shielding while being flexible and conformable.

Custom Manufacturing
Custom Knitted Wire Mesh Gaskets
1.Material selection:
Choose conductive wire material (e.g. copper, aluminum, stainless steel)
Select appropriate gauge (thickness) for desired flexibility and strength
2.Knitting process:
Knit the wire into a mesh pattern
Adjust stitch count to control density and shielding effectiveness
3.Shaping:
Die-cut to desired shape using custom dies
May involve folding, layering, or coiling for specific applications
4.Finishing:
Clean and inspect for defects
Apply coatings or treatments if needed
5.Testing:
Measure shielding effectiveness
Test physical properties (compression, resilience, etc.)
6.Customization:
Adjust mesh density, wire diameter, or shape as needed
Combine with other materials (foam cores, adhesives) if required
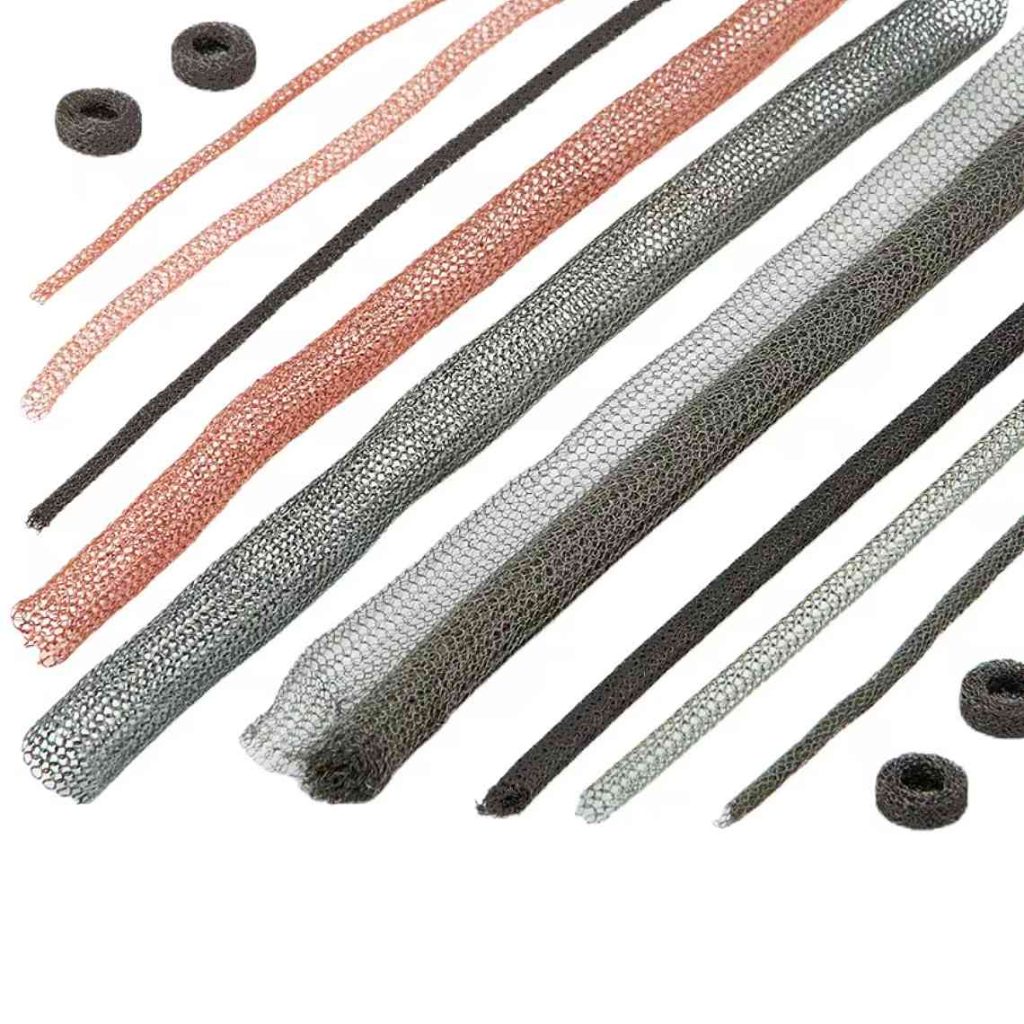

Steps to Determine Size of
Knitted Wire Mesh Gaskets
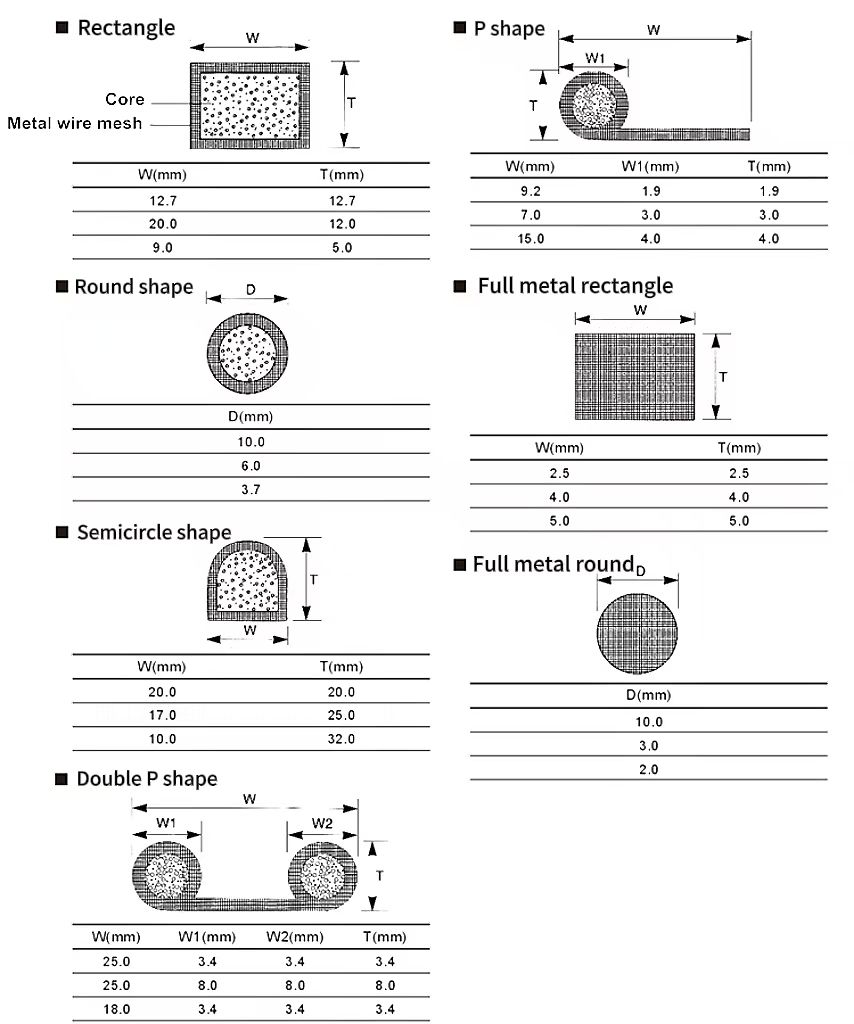
1.Determine the required land area: Incorporate additional clearance around the flange dimensions to ensure proper accommodation of the gasket.
2.Select appropriate standard sizes: Consult the provided table of standardized round gasket dimensions.
3.Evaluate custom options: If standard sizes are unsuitable, discuss custom-sized gaskets with manufacturers.
4.Consider mounting methods: Ensure sufficient space is allocated for the selected mounting techniques (e.g., adhesive-backed, slot mounting, groove channel mounting).
5.Assess shielding effectiveness: Confirm that the chosen size meets the necessary shielding performance criteria based on application requirements.
6.Account for thermal expansion: Factor in potential thermal expansion of the flanges when determining gasket size.
7.Follow manufacturer guidelines: Consult gasket manufacturers for specific recommendations tailored to your application.
Knitted Wire Mesh Gaskets Manufacturing
Here’s a simplified overview of how to manufacture knitted wire mesh gaskets:
1.Start with raw wire material (like metal).
2.Knit the wire into a mesh pattern. The mesh is usually measured by how many stitches are in a certain area.
3.Group the mesh into categories like fine, medium, standard, coarse, etc.
4.Use different post-knitting processes to shape the mesh:
- Coiling: Rolls up the mesh into spirals for shipping
- Folding/Layering: Builds up pads of mesh
- Crimping: Uses rollers to make anti-vibration products
- Pressing: Compresses the mesh in dies to create precise shapes
- Spiralling/Milling: Creates long, continuous pieces by rolling
5.Cut the mesh into the desired shape and size.
6.Test for proper fit and shielding performance.

Key Factors to Consider in Sealing Applications
1.Flange Dimensions:
Accurately measure the dimensions of the flanges or surfaces that require sealing to ensure precise fit and optimal performance.
2.Compression Requirements:
Evaluate the specific compression force needed for the application. For instance, applications with extended lengths may require lower compression, while rigid structures necessitate higher compression forces.
3.Shielding Needs:
Assess whether magnetic field shielding is required in addition to electrical field shielding to protect against electromagnetic interference.
4.Environmental Factors:
Consider environmental conditions such as temperature ranges, humidity levels, and potential exposure to corrosive substances to ensure material durability and longevity.
5.Material Compatibility:
Verify that the selected material is compatible with the surrounding environment and does not react adversely with other components, ensuring long-term stability and reliability.
Need a Large Order?
We can design and manufacture a component for your specific application in any quantity. For quantities over 1,000, please request a quote.

RECENT PRODUCT
-
Handa Shielding TCS Dual-Wing Wire Mesh Core Technology: TCS Material InnovationDual-Wing Structural DesignTechnical SpecificationsApplications1. Aerospace and Defense2. Medical Devices3. Telecommunications4. Industrial ElectronicsCustomization and......
-
Knitted Wire Mesh Gaskets 1. Introduction2. Product Overview2.1 Construction2.2 Standard and Custom Sizes3. Key Features3.1 Excellent Sealing Performance3.2 EMI Shielding3.3 High - Temperature......
-
Knitted metal wire mesh gaskets are engineered using fine metal wires, typically stainless steel or other conductive alloys, that are knitted or woven......