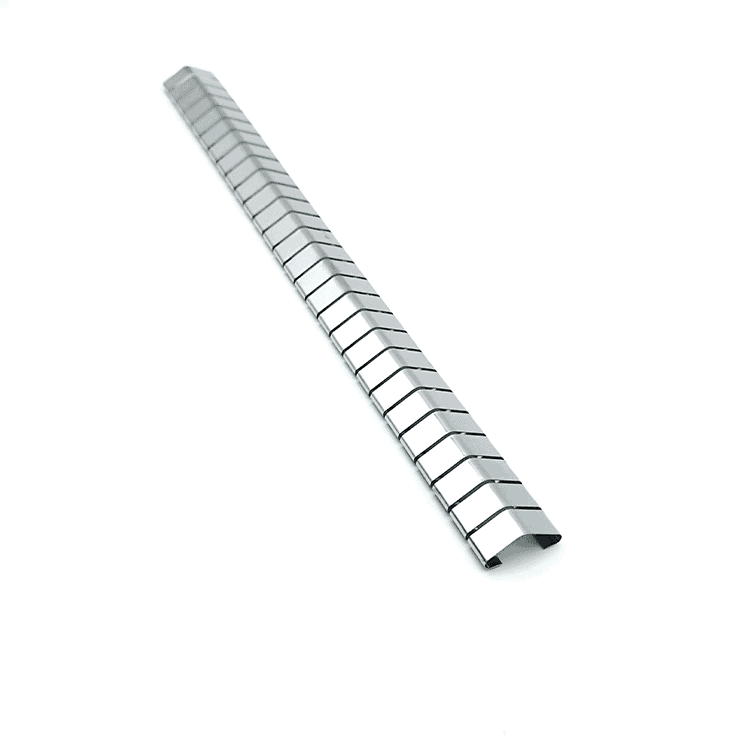
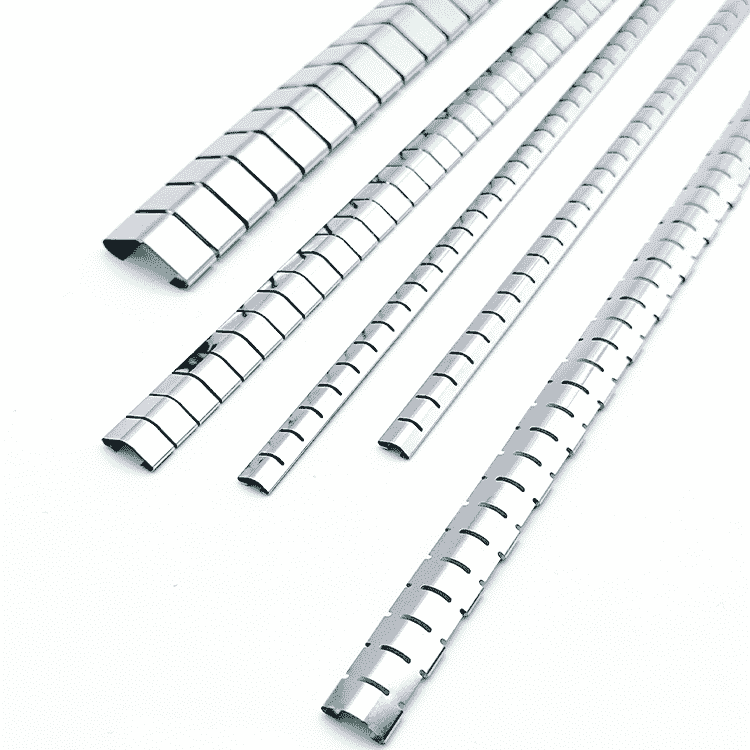
ユニークなカントコイル設計によるEMIシールドカントコイルスプリング
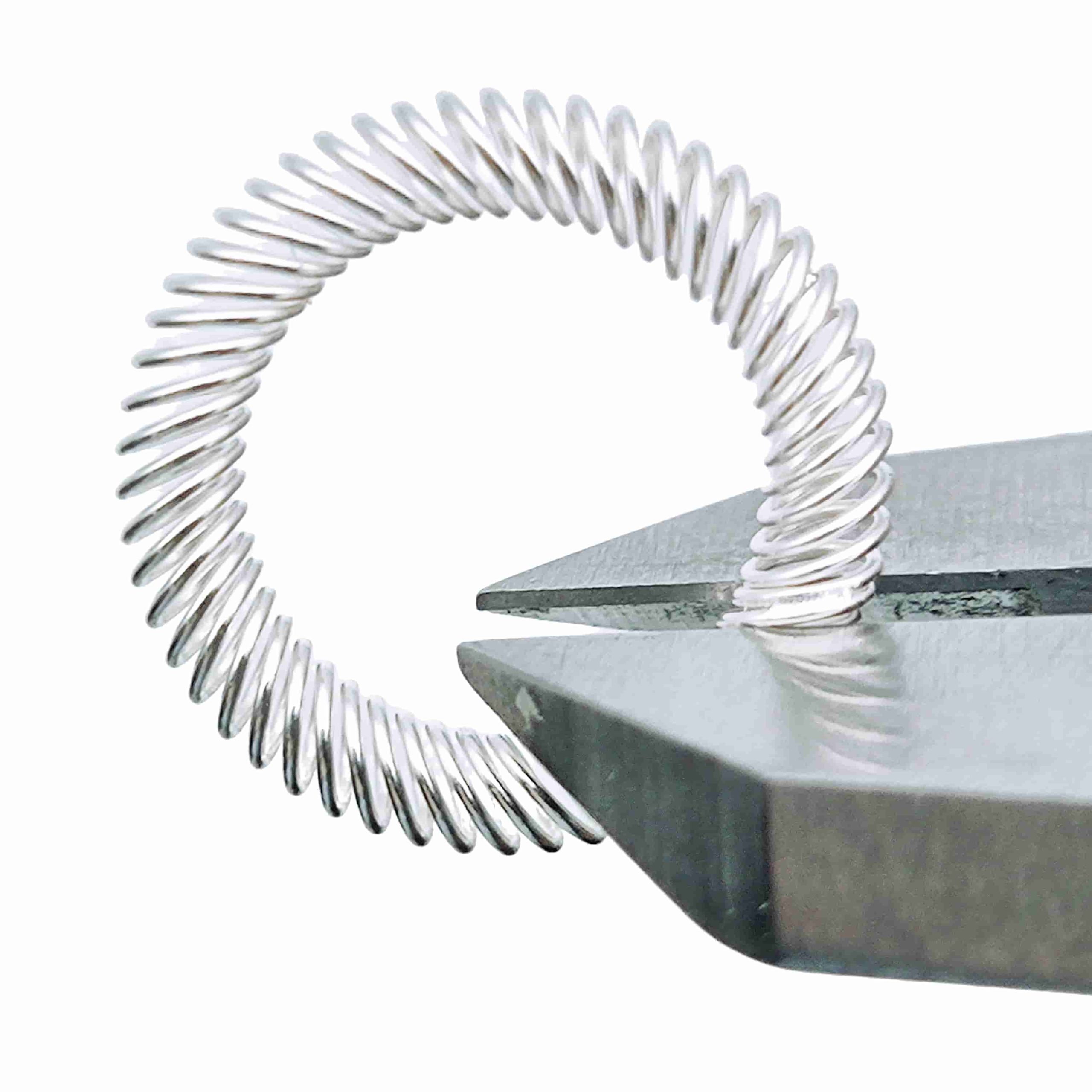



EMIシールドカントコイルスプリングとしても知られている。 コイルスプリングこの革新的なコンポーネントは、効果的な設計が施されている。 でんじぼうがい そして 無線周波数干渉(RFI) シールドと同時にメカニカルスプリングとしても機能します。これらのスプリングはユニークなカントコイル設計が特徴で、優れたEMIシールド、機械的ラッチ、導電性のために複数の接点を提供することができます。
EMIシールドカントコイルスプリングとしても知られている。 コイルスプリングこの革新的なコンポーネントは、効果的な設計が施されている。 でんじぼうがい そして 無線周波数干渉(RFI) シールドと同時にメカニカルスプリングとしても機能します。これらのスプリングはユニークなカントコイル設計が特徴で、優れたEMIシールド、機械的ラッチ、導電性のために複数の接点を提供することができます。
目次
EMIシールド・カント・コイル・スプリングとは?
EMIシールドスプリングは、EMIシールドとEMIシールドの両方の機能を持つ特殊なスプリングです。 機械的および電磁的シールド能力.そのカント・コイル設計は、コイルが斜めに配置されているのが特徴で、圧縮されたときに複数の接点が生まれます。これにより、スプリングは機械部品としてだけでなく、非常に効果的なEMI/RFIシールドとしても機能します。
電磁干渉は現代の電子機器において重要な問題であり、外部または内部のEMIは信号を乱し、性能に影響を与えます。EMIシールドスプリングは、EMIやRFIから敏感な電子部品を保護すると同時に、導電性、接地性、安全なラッチなどの機械的、電気的な利点を提供するように設計されています。
EMIシールド・カント・コイル・スプリングの主な特長
- 二重機能(スプリングとシールド):の特徴のひとつ。 EMIシールド・スプリング は、スプリングとEMI/RFIシールドの両方の役割を果たす能力を持っています。この二重の機能性により、コンパクトな電子設計において非常に多用途で価値のあるものとなっている。
- 複数のコンタクトポイント:カント型コイルデザインにより、複数の接点が設けられ、導電性とシールド性能が向上しています。これらの複数の接触点は、衝撃、振動、その他の機械的ストレス下でも、一貫した信頼性の高い接触を保証します。
- 広いEMIスペクトル減衰:EMIシールドスプリングは、高周波EMIを含む幅広い周波数に高い効果を発揮します。そのため、小型パッケージや高周波信号で信頼性の高いシールドが必要なアプリケーションに特に適しています。
- 特定のインピーダンスに調整可能:EMIシールドスプリングは、特定のインピーダンス要件を満たすようにカスタマイズすることができます。これは、最適な電気的性能を確保するためにインピーダンス整合が必要なアプリケーションでは特に重要です。
- 多機能能力:EMIシールドに加え、これらのスプリングは次のような役割も果たします。 メカニカルラッチ そして 導電性 部品に使用される。この汎用性により、コネクター、ラッチ、アース用途に最適です。

EMIシールドカントコイルスプリングの用途
EMIシールドカントコイルスプリング は、さまざまな業界の幅広い用途で使用されています。繊細な電子機器を干渉から保護すると同時に、機械的機能を提供するその能力は、以下の分野で非常に貴重なものとなっています:
1. 電子エンクロージャー
電子機器はしばしばEMIを発生させ、他の部品や外部機器と干渉する可能性があります。EMIシールドカントコイルスプリングは一般的に以下の用途に使用されています。 電子筐体 効果的なシールドを提供し、不要な電磁信号の漏洩や侵入を防ぎます。エンクロージャー、ドア、パネルのエッジに組み込むことで、適切なシールドとアースを確保することができます。
2. 電力管理システム
自動車、航空宇宙、産業用アプリケーションの電源管理システムは、EMIの影響を非常に受けやすい。EMIシールド コイルスプリング これらのシステムでは、電磁干渉が変圧器、レギュレーター、配電ユニットなどの重要なコンポーネントの性能に影響を与えないようにするために使用されます。
3. アンテナベース
アンテナシステム、特に通信機器では、シグナルインテグリティを確保するために正確なシールドが必要です。EMIシールドスプリングは アンテナベース 干渉を最小化し、アンテナが支障なく信号を送受信できるようにするため。
4. 導波管フランジ
導波管のような高周波システムでは、EMIシールドスプリングは適切な電磁分離を維持し、信号漏れを最小限に抑えるために使用されます。その柔軟性と凹凸のある表面に適合する能力は、導波管フランジやその他の高周波コンポーネントのシールに理想的です。
5. 同軸および電気コネクター
EMIシールド・スプリングは、一般的に次のような場所で使用されている。 同軸および電気コネクター電気的接触とEMIシールドの両方を提供することで、二重の目的を果たします。外部干渉から接続をシールドしながら、コネクターインターフェース間の一貫した導電性を維持するのに役立ちます。
6. 医療機器
医療機器において、EMIシールドは繊細な電子部品の安全性と信頼性を確保するために非常に重要です。EMIシールドカントコイルスプリングは、画像処理システムや監視装置などの医療機器に使用され、コンパクトなフォームファクターを維持しながら、信頼性の高いシールドと電気的接続を提供します。
7. 航空宇宙・防衛
航空宇宙産業や防衛産業では、信頼性の高い性能を提供しながら、過酷な環境条件に耐える部品を必要とすることがよくあります。EMIシールドキャントコイルスプリングは、電子システムを干渉から保護し、重要なシステムが中断することなく機能することを保証するために、様々な航空宇宙および防衛アプリケーションで使用されています。

EMIシールドカントコイルスプリングの素材と構造
のパフォーマンス EMIシールドカントコイルスプリング は、その構造に使用される材料によって大きく左右される。一般的な素材は以下の通り:
1. 銅合金
銅合金はその優れた導電性と耐食性により、EMIシールドスプリングに頻繁に使用されています。銅合金スプリングは信頼性の高いEMIシールドを提供し、導電性と耐食性が主な懸念事項である多くの用途で無メッキで使用されます。
2. ステンレス鋼
ステンレス鋼はその強度と耐久性で知られており、過酷な環境条件に耐える必要のあるEMIシールドスプリングに最適です。ステンレス鋼は銅ほど導電性ではありませんが、ニッケルや金などの導電性金属でメッキすることにより、EMIシールドや電気接点用途での性能を向上させることができます。
3. ベリリウム銅
ベリリウム銅は、高強度、耐食性、導電性というユニークな組み合わせを提供します。そのため EMIシールドカントコイルスプリング ベリリウム銅スプリングは、航空宇宙や軍事用途のような過酷な環境で使用されます。ベリリウム銅スプリングは、金、銀、または他の導電性材料でメッキすることも可能です。
4. ニッケルめっき
耐食性と導電性を高めるため、一部のEMIシールドスプリングはニッケルメッキが施されています。ニッケルメッキされたスプリングは、電気的性能と耐久性のバランスが良く、過酷な環境での使用に適しています。
EMIシールドカントコイルスプリングの利点
EMIシールド・スプリング は、EMI/RFIシールドや機械的用途に非常に効果的な数多くの利点を提供します。以下のような利点があります:
1. 効果的なEMI/RFIシールド
EMIシールドカント付きコイルスプリングの主な利点は、電磁波や無線周波数の干渉に対して信頼性の高い保護を提供できることです。カンテッドコイル設計により、幅広い周波数帯域で安定したシールド性能を発揮するため、高周波信号を使用するアプリケーションに最適です。
2. ストレス下でも信頼できるコンタクト
EMIシールドカントコイルスプリングは、衝撃、振動、移動の条件下でも、相手表面との一貫した接触を維持するように設計されています。これは、他のタイプのスプリングが故障する可能性のある動的な環境において、信頼性の高い電気的性能と機械的ラッチを保証します。

3. 優れた減衰
これらのスプリングは 優れた減衰 は、特に高周波用途において、EMI スペクトラム全体にわたって優れている。このため、スペースが限られているが高いシールド性能が求められる小型電子機器に最適である。
4. 特定の要件に合わせてカスタマイズ可能
EMIシールドキャントコイルスプリングは、特定のインピーダンスと電気的要件を満たすように調整することができ、各アプリケーションに最適な性能を保証します。カスタマイズ可能な設計により、エンジニアは特定の使用ケースに必要な正確な寸法、力、電気特性を指定することができます。
5. 多機能:
シールドに加えて、EMIシールドカントコイルスプリングは、次のような複数の役割を果たすことができます。 メカニカルラッチ, 電気伝導度そして 接地.この汎用性により、複数のコンポーネントの必要性が減り、設計が簡素化され、コストが削減される。
EMIシールドカントコイルスプリングの規格準拠
EMIシールドスプリングは、様々な産業や用途で信頼性の高い性能を発揮するために、国内外の様々な規格に適合するように設計されています。 EMC(電磁両立性) そして 電磁妨害 規格があります。これらには以下のものが含まれる:
- CISPR:無線周波数の干渉を制御するための国際規格。
- IEC 61000:電気・電子機器の電磁適合性規格。
- 国際標準化機構:国際標準化機構(International Organization for Standardization) : 国際標準化機構(International Organization for Standardization)による、電子機器や自動車を含む様々な産業向けの規格。
- SAE:自動車技術会(Society of Automotive Engineers)が定めた自動車用電子機器の規格。
- FCCパート15:無線周波数エネルギーを放出する機器に関する米国連邦通信委員会の基準。
- MIL-STD:電磁干渉および環境条件に関する米軍規格。
これらの規格に適合することで、EMIシールドカントコイルスプリングは干渉から効果的に保護され、各業界の規制要件に適合します。
EMIシールドカントコイルスプリング使用時の考慮事項
一方 EMIシールド・スプリング には多くの利点があるが、留意すべき重要な点がいくつかある:
1. デザインの複雑さ
EMIシールドスプリングの設計は、コイル寸法、圧縮力、シールド効果などの要因を慎重に考慮する必要があります。エンジニアは、最高の性能を提供するために、スプリングの設計が特定のアプリケーションに最適化されていることを確認する必要があります。
2. 素材の選択
を選択する。 適材 導電性、耐食性、機械的強度の望ましいバランスを達成するためには、スプリングの材質が重要です。使用環境と電気的要件により、異なる材料とコーティングが必要になる場合があります。
3. 設置条件
EMIシールドキャントコイルスプリングが期待通りの性能を発揮するためには、適切な取り付けが不可欠です。アプリケーションによっては、スプリングを正しく設置し、安定した接触を維持するために、特殊な工具や技術が必要になる場合があります。
4. コストに関する考察
EMIシールドキャントコイルスプリングは重要な利点を提供する一方で、従来のシールドソリューションよりも高価になる可能性があります。しかし、長期的な信頼性、多用途性、多機能性により、初期費用は相殺されます。

結論
EMIシールド・スプリング は、繊細な電子機器を電磁波や無線周波数の干渉から保護するための非常に効果的なソリューションです。そのユニークな傾斜コイル設計は、一貫したシールド、電気伝導性、機械的ラッチのための複数の接点を提供し、航空宇宙や防衛から医療機器や家電に至るまで、多くの産業で貴重な部品となっています。
EMIシールドスプリングは、信頼性の高いEMI/RFI減衰、多機能、過酷な環境への耐性を提供することで、機械的安定性を確保しながら電子部品を干渉から保護したいエンジニアにとって、多用途で信頼性の高い選択肢です。
こちらもおすすめ
-
EMIシールド効果に優れた多用途スティックオン取付フィンガーストリップ
EMI/EMCシールド|RFIシールド|EMIガスケット
フィンガーストリップ
電磁干渉(EMI)は電子機器やシステムに重大な問題を引き起こし、性能低下や誤動作、さらには故障につながる可能性があります。そこで、特に薄型の双方向アプリケーションに不可欠なEMIシールド・ソリューションとして、貼り付け式取り付けフィンガーストリップが登場しました。
-
 高いEMIシールド効果 スナップオン取付フィンガーストリップ
高いEMIシールド効果 スナップオン取付フィンガーストリップEMI/EMCシールド|RFIシールド|EMIガスケット
フィンガーストリップ
スナップオン取付フィンガーストリップは、様々な電子筐体やアセンブリに使用される非常に効果的な電磁干渉(EMI)シールド部品で、電磁的完全性を確保し、無線周波数干渉(RFI)を防止します。電子システムの進歩に伴い、EMIシールドは... 続きを読む
-
 汎用性が高く、欠かせない導電性銅箔テープ
汎用性が高く、欠かせない導電性銅箔テープEMIテープ、EMCホイル、導電性織物、半導電性不織布
銅箔テープ
導電性銅箔テープは、エレクトロニクスから自動車まで幅広い産業で幅広く使用されている、汎用性の高い不可欠な素材です。導電性と粘着性のユニークな組み合わせにより、様々な用途の効率的なソリューションとして機能します。
-
 導電性アルミ箔テープ
導電性アルミ箔テープEMIテープ、EMCホイル、導電性織物、半導電性不織布
導電性アルミテープ
導電性アルミ箔テープは、様々な産業、特にエレクトロニクス、電気工学、建築において汎用性が高く、必要不可欠な材料である。この記事では、導電性アルミ箔テープの特性、用途、利点、選択基準について深く掘り下げる。
-
 高いシールド効果 EMIシールドフィンガーストックガスケット
高いシールド効果 EMIシールドフィンガーストックガスケットEMI/EMCシールド|RFIシールド|EMIガスケット
フィンガーストリップ
ますます複雑化する今日の電子環境において、電磁干渉(EMI)シールドはデバイスメーカーや設計者にとって重要な関心事となっています。EMI問題に対処するための効果的なソリューションのひとつが、高いシールド効果を持つEMIシールドフィンガーストック/フィンガーストリップガスケットの使用です。これらの特殊な......